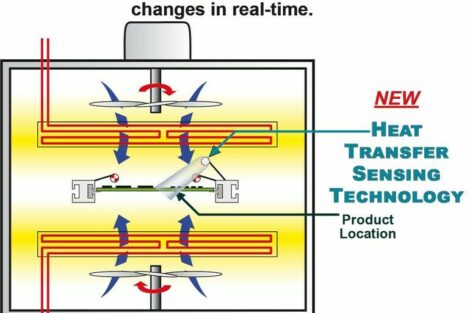
Heat management in electronic systems include silicone/silicone-free pastes (greases), adhesives, RTVs and epoxy resins. Increasing miniaturisation in electronics means that heat dissipation problems are becoming increasingly important. Thermal protection systems address these problems by providing excellent heat transfer properties to ensure that heat flows from the component into the metal heatsink at the fastest rate possible
A non-silicone Heat Transfer Compound (HTC) has been developed for efficient thermal coupling of electrical and electronic components. HTC provides non-creep characteristics and excellent thermal conductiv- ity even at high temperatures: 0.9 W/m.K.
HTC has a broad operating temperature range (–50 ºC to +130 ºC) and offers low toxicity. Non-silicone Heat Transfer Compound Plus (HTCP) provides even higher thermal conductivity than HTC at 2.8 W/m.K and also displays superior heat transfer characteristics.
Silicone based pastes, such as HTS and HTSP, have higher operating temperatures than non-silicone alternatives. The silicone Heat Transfer Compound (HTSP) is an extremely thermally conductive paste for special applications where thermal management is critical. Operating over a wide temperature range (–50 ºC to +200 ºC), HTSP is a metal oxide filled silicone oil providing thermal conductivity at 3.0 W/m.K.
It may be sufficient to ensure thermal control, with heat generating circuitry, by potting into a metal box using a thermally conductive potting compound.
The flame retardant ER 2074 epoxy resin exhibits superior thermal conductivity and is completely free of abrasive fillers such as alumina. ER 2074 ensures substantially less wear on mix and dispense and other processing equipment. The system shows low viscosity when mixed, and the exotherm temperature rise on curing is low.
EPP EUROPE 430
Share: