The PXI platform is well known for its many solutions for implementing the switching requirements required for ATE systems. Almost all of these are based on mechanical relays which rely on plated mechanical contacts. There is a large range of solutions in the PXI format from a variety of companies. Until recently solid state switching was not widely offered in PXI, but with the addition of two solid state switching cards to their range Pickering Interfaces are starting to open up new opportunities.
The highest performance relays are based instrument grade reed relays. The “moving” part of these relays is a blade contact deflected by a magnetic field contained within a hermetically sealed glass envelope with the contact materials being plated ruthenium one the highest performance models. These relays have an excellent mechanical life (more than 1 billion operations) and stable contact resistance at low and medium currents. Operating life reduces as the switching current increases, and switching current is typically limited to the region of 0.5 A to 1.2 A. Operating speed is fast, with relays typically capable of 250 µs opening and closing times.
Electro-mechanical relays (EMR) can offer higher current ratings, but usually with lower mechanical life because of the presence of moving parts. Operating speeds are slower than reed relays with a typical small EMR having an operating time of 3 ms and larger relays having longer operating times. Many EMR’s are not well suited to low level switching since the lack of a truly hermetic seal results in surface contamination that can lead to high contact resistance if the contacts are not wetted by the signal current. They are generally more robust than reed relays to higher current surges and have a lower contact resistance. Until recently solid state switching was not widely offered in PXI, but with the addition of two solid state switching cards to their range Pickering Interfaces are starting to open up new opportunities. There are a considerable number of types of solid state relay, varying CMOS types at the higher resistance end to large FET switches for higher currents. Two types of switch have been added to the PXI range.
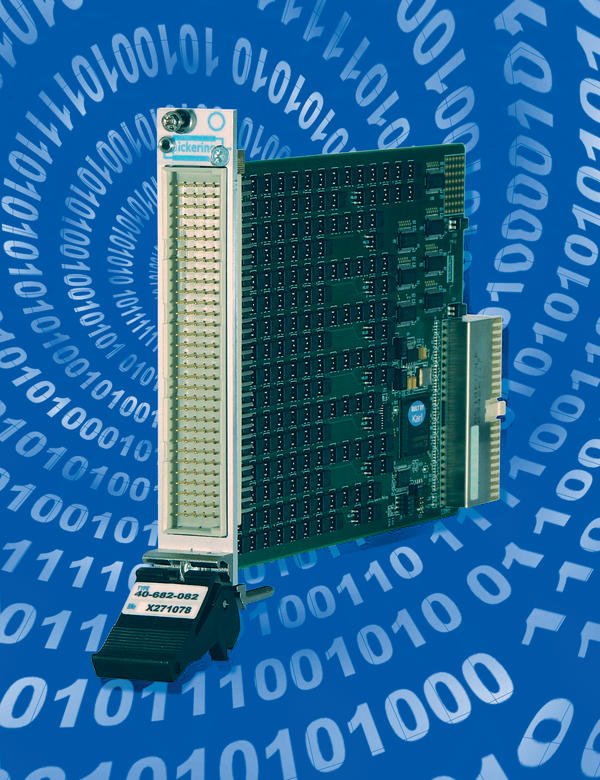
The first is a CMOS switch which is incorporated into the 40–680. This switching module offers a dense multiplexer solution with typically 150 W on resistance and 20 mA operating current. It is ideal for data acquisition applications where uses need to select one of many channels and connect it to a single instrument. These switches are fault protected, they automatically turn themselves off if the signal exceeds the rated input voltage and automatically turn themselves off the PXI module power supply becomes disconnected. The former characteristic is unique to these switch types, the latter is what is expected to happen when mechanical relays are used. The switch operating speed is very fast, much less than 1 µs, and free from contact bounce so they are much faster than even reed relays. They can be used to provide extremely dense switching solutions since the PCB footprint is small.
The second type of solid state switch to be introduced is the 40–682, a configurable MUX with the same functional performance as its 40–612 versatile MUX which uses EMRs. The switches used in the 40–682 have a 250 mA continuous rating and a rating of 750 mA for 100 ms. Contact resistance for each switch is typically less than 1 W and for a typical path is 3.2 W. Operating speed for the solid state relays in 40–682 is fast compared to an EMR or reed relay at less than 20 µs and the current carrying capability is good. Lifetime is unaffected by the switching current provided it is operated within its rated characteristics. The relay can endure switching of capacitive loads with less degradation of life than is often typical of mechanical relays. To provide this level of performance the switching element is relatively large (but much smaller than a mechanical relay) so the device has more capacitance than a relay. As a result operating bandwidth is limited to 1 MHz by the degradation in isolation when measured in a 50 W system. Because of the small footprint of the switching device the enterprise is able to offer other solid state solutions using this switch and variations with higher operating current. Designers now have a wider choice of switching technologies to chose form in PXI, all of which have their own areas of excellence and compromise.
EPP Europe 449
zusammenfassung
Die PXI-Plattform ist bekannt dafür, dass sie vielfältige Lösungen zur Erfüllung der Schaltungsanforderungen von ATE-Systemen bietet. Mit der Hinzunahme von zwei Festkörperschalter-Baugruppen in ihre Produktpalette eröffnet die Firma Pickering Interfaces Entwicklern nun neue Chancen.
La plate-forme PXI est connue pour proposer des solutions variées satisfaisant aux exigences de commande des systèmes ATE. Avec l’ajout de deux modules de circuits intégrés à semi-conducteur à sa gamme de produits, la société Pickering Interfaces ouvre de nouvelles perspectives.
La piattaforma PXI è conosciuta per le molteplici soluzioni che offre ai requisiti di commutazione dei sistemi ATE. Con l’aggiunta di due schede switch a stato solido alla propria gamma prodotti, la ditta Pickering Interfaces offre oggi nuove opportunità agli sviluppatori.
Facts and figures
Pickering Interfaces is a market innovator in signal switching and conditioning for a broad range of applications and architectures, with a large range of switching cards for PXI, LXI, PCI, VXI and GPIB applications. The enterprise has provided solutions to both commercial and military applications. In addition, its range of instrumentation provides innovative test solutions to users and integrators of modular test systems. The company operates globally with direct operations in the U.S., UK, Germany, Sweden, France, Czech Republic, and engineering support in China, together with additional representation in countries throughout the Americas, Europe and Asia.
Share: