Following mechanisation, mass production, and computerised automation, the fourth industrial revolution (Industry 4.0) is transforming traditional automation into cyber-physical systems. Surface-mount electronics manufacturing has a leading role in the revolution: not only are the instruments of Industry 4.0 built here – from tiny smart sensors to Internet infrastructure and high-performance Cloud servers – but also advanced inline automation is combined with powerful software applications to implement smart manufacturing that adapts continuously to optimize productivity.
It’s all about the data
In today’s electronics manufacturing services (EMS) businesses, the traditional boundary between factory floor and back office is disappearing as more and more manufacturing data is harvested and analysed to reveal new insights for further enhancing efficiency, quality and productivity.
The production line may combine equipment such as dispenser or screen printer, mounters and optical inspection from a number of different manufacturers. Although there are industry standards that allow basic communication between the various machines, interfaces between equipment from different vendors often cannot support the information exchanges needed to enable smart manufacturing.
Yamaha‘s Motor Intelligent Machines Division has created its own specification for a machine-to-machine interface that enables real-time data exchanges between inline surface-mount equipment. Moreover, a complete set of software applications capture and analyse the data.
Seamless Connection of Enterprise Assets
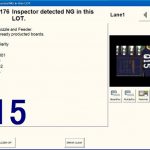
Among these software applications, the company’s QA Option is hosted on the line and compares post-placement inline optical inspection (AOI) data with dispenser/printer and mounter data (figure 1) to pinpoint any component-placement errors or solder-paste defects down to the level of individual mounter nozzles or stencil apertures. Notifications presented on-screen (figure 2), or pushed to the supervisor’s own device via the company’s Mobile Judgement software, enable immediate remedial action, and hence improve quality control and drive-up productivity. The information gathered has also been able to drive predictive maintenance, which is also now seen as an important aspect of smart manufacturing.
In addition to these applications, the company has developed the Y.FacT factory software suite, including setup, monitoring and traceability tools.
By facilitating setup, the S-Tool utility helps manage materials that may otherwise deteriorate over time. Automatically monitoring stock age and condition helps exclude any unsuitable materials from finished products. By recording data such as the board code, solder paste type, and the identities of component feeders and reels, S-Tool can help prevent errors and improve product quality. When assembling LED-lighting products, for example, checking the LED brightness (BIN), colour temperature and illumination pattern indicated on product barcodes helps prevent building assemblies using parts that are not closely matched. It can also connect to any component tower storage system, and use parts-remaining information from machines in the line to coordinate reel and feeder changes to ensure timely replenishment and minimize stoppages.
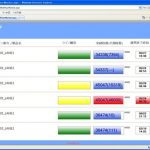
Monitoring equipment in each line and across the factory using M-Tool enables checking of status via a web-based interface to assess detailed information such as efficiency, operating ratios and pickup rates in real time. Figure 3 shows how colour-coded status enables fast and easy monitoring of line status. It is an easy next-step to consolidate this data automatically into reports for storage and analysis by higher-level applications running in the Cloud.
The traceability application, T-Tool, records each individual assembly identifier with its associated board identity and component data for every placement on the board. This is one area the underlying data structure of the surface-mount equipment is critical for handling the detailed component-level information. The company’s proprietary data structure can record component serial numbers as well as position data and the PCB serial number and transfer the information through a shop-floor system into a traceability database.
Conclusion
Businesses are making the move into smart manufacturing to deliver high-quality products to global markets at competitive prices, while at the same time meeting market demands for large numbers of product variants and options to customize or individualize. Inter-machine communications hold the key to extracting the data needed to analyse performance, and communicating the changes necessary to adapt quickly and efficiently.
Share: