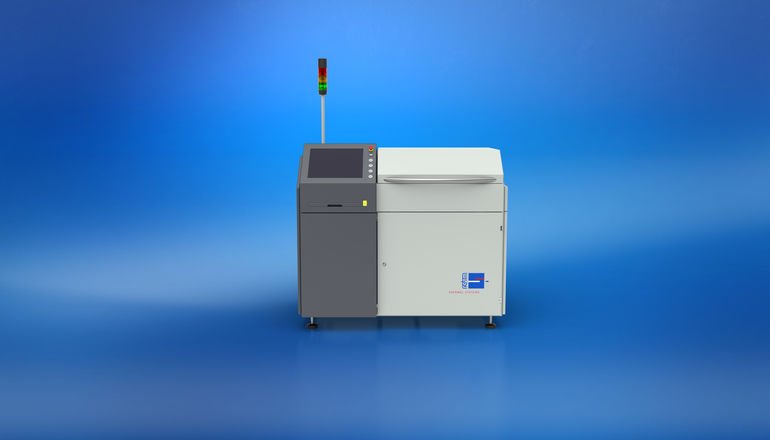
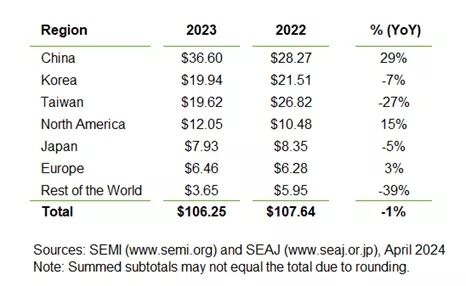
(Updated on 05.01.2021) The Nexus soldering system guarantees the best results with a reflow soldering process using contact heat under vacuum. This enables the Nexus to meet the highest requirements in the field of advanced packaging and power electronics. The contact soldering system under vacuum is also best suited for void-free soldering of different components (e.g. IGBT) on DBC substrates. The substances are usually joined from different raw materials under vacuum at temperatures of up to 450 °C – the optimum solution for void-free and flux-free applications. The Nexus from Rehm Thermal Systems thus not only benefits the soldering process, but also all other thermal processes.
A major benefit of the Nexus contact soldering system is that the heating or cooling gradient can be predefined based on predetermined parameters. The gradients can be preset as required. Within these specification limits, the temperature is adjusted automatically by the system to ensure these limit values are not exceeded. This rules out any possible malfunction of the assembly to be soldered. The heating output of the Nexus has been designed for a uniform heating process when fully loaded with high-mass assemblies, meaning that short cycle times are also no problem. Sensor components determine and verify the temperatures recorded on the goods carrier support.
Reliable vacuum processes for improved quality
Vacuum soldering achieves productivity increases and quality advantages in the manufacturing of power electronics. In this way, the vacuum ensures oxide-free processes, as well as improved wetting and thus better filling of soldered joints. In addition, the vacuum drastically reduces the voids in soldered joints and enables processes such as plasma cleaning and atmosphere exchange in advanced packaging. The reduced pressure helps, among other things, to minimise oxidation on the components and on the joints themselves. The heat is transferred both via thermal conduction and optionally by radiation. Its compact dimensions and high user-friendliness make the Nexus particularly suitable for use in small-scale and medium-scale production, as well as in laboratories.
Inert gases and forming gas
Nitrogen (N2) is typically used to protect against oxidation. In combination with 5 % hydrogen, the forming gas is also used for reducing oxides; no special safeguards are necessary within this mixing ratio. Forming gases with a hydrogen content from 5 % to 100 % need necessarily appropriate safeguards and are used only at 280 °C or higher. Depending on the process temperature, the use of formic acid can be beneficial. For a stable, reliable, flux-free soldering process, the inert carrier gas (N2) is enriched with formic acid (HCOOH) and routed into the process chamber.
Flux-free soldering and deoxidation
For stable, flux-free soldering or removal of oxides, the inert carrier gas (N2) is enriched with formic acid (HCOOH) and routed into the process chamber. To keep the “saturation” of the carrier gas with formic acid constant, the parameters must remain constant while the liquid formic acid is flowing through. These include the flow velocity, flow rate, temperature and the filling capacity of the formic acid tank (bubbler). Thanks to today’s control engineering, the nitrogen flow rate can be monitored easily and reliably – unlike the formic acid level in conventional bubbler solutions. These conventional bubblers must be refilled manually with the acid – with due consideration of the safety precautions for employees – and are subject to greater fluctuations in the filling quantity. More advanced is the new generation of bubblers used by Rehm Thermal Systems – these control and readjust the fill level automatically. By increasing the temperature of the formic acid in the bubbler, a higher accumulation of formic acid in the nitrogen can easily be attained.
Oxides on metals are removed using formic acid as described below. So-called formates of the metal form initially – and from about 200 °C these formates are decomposed (Cu) or evaporated (SnO, SnO2). The H+ formed in the second part assists the oxide removal. An oxide-free and highly wettable surface on copper and other metals can therefore be achieved – typically for a subsequent soldering process in the plant or for downstream processes. The application is suitable from process temperatures of 200 °C.
Oxygen analysis for process monitoring
The analyser allows you to permanently monitor the oxygen content in the process chamber during almost all process steps. This ensures that inerting remains effective, while the process chamber remains leakproof.
Rehm Thermal Systems GmbH
Leinenstraße 7
89143 Blaubeuren-Seissen Germany
Tel.: +49 7344 9606–0
E-Mail: info@rehm-group.com
Website: www.rehm-group.com